INTRODUCTION
Thyroid Function
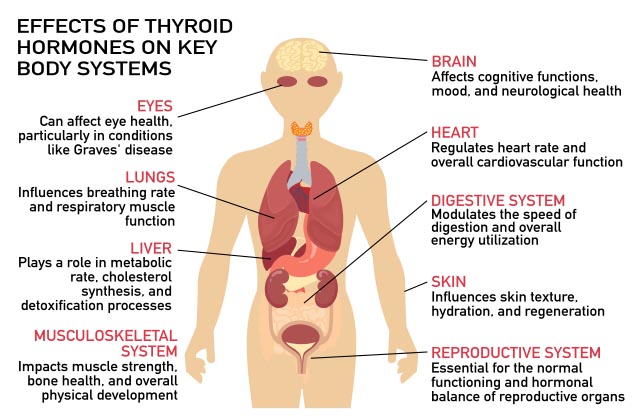
In our Thyroid Health 101 series, we explored the critical role of the thyroid gland, a vital gland that regulates key body processes through hormone production. Now, transitioning from understanding to practical application, Thyroid Health 102 focuses on the essential strategies for managing thyroid health effectively. Discover how to navigate the challenges of both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular health monitoring.
Managing Thyroid Health
Effective management of thyroid health requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary adjustments, targeted medication, consistent monitoring, and the use of both traditional and telehealth medical consultations. Whether dealing with hypothyroidism (underactive conditions) or hyperthyroidism (overactive conditions), these strategies are vital for maintaining balance and enhancing your quality of life.

Effective management is not just about addressing the dysfunction—it's about embracing an integrated approach that enhances your overall wellbeing and quality of life. Each person's journey with thyroid health is unique, and managing it effectively means paying attention to the body's signals and responding with appropriate health strategies. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge to take control of your thyroid health and advocate for your well-being in a proactive and informed manner.
REGULAR MONITORING AND TESTS FOR THYROID HEALTH
For individuals diagnosed with thyroid disorders, regular monitoring is a critical component of effective management. It involves a variety of tests and self-checks designed to track the progress of treatment and detect any changes that may require adjustments in therapy. Here, we explore the importance of these monitoring practices and how they contribute to the optimal management of thyroid conditions.
Key Components of Thyroid Health Monitoring
- Self-Checks: Regular self-examinations of the neck can be a proactive way to monitor for physical signs of thyroid issues, such as:
- Thyroid Enlargement: Checking for any noticeable increase in size that might indicate goiter or other thyroid abnormalities.
- Nodules:Identifying any unusual lumps which might necessitate a visit to your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
- Blood Tests: Regular thyroid function tests are fundamental to managing thyroid health. These tests typically measure Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Free Thyroxine (T4), and Triiodothyronine (T3) levels. They are crucial for:
- Adjusting Medications: Proper dosing of thyroid medications depends on the levels of thyroid hormones in your blood. Regular testing helps ensure that you are receiving the correct dosage.
- Evaluating Treatment Effectiveness: Tracking changes in hormone levels over time allows healthcare providers to determine how well the current treatment regimen is working and make necessary adjustments.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound examinations of the thyroid gland play a significant role in thyroid management by:
- Detecting Structural Changes:Ultrasounds can reveal changes in the gland's structure, such as growth or reduction in size, which may impact hormone production.
- Identifying Nodules or Tumors: These tests are vital for detecting the presence of nodules or tumors, some of which may require further testing to rule out cancer.
The Importance of Consistent Monitoring
Regular monitoring is essential not only for adjusting treatment plans but also for early detection of potential complications. Consistent check-ups and tests help in:
- Early Detection: Catching issues early can lead to more effective management and better outcomes.
- Long-Term Health Maintenance: Ongoing monitoring is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing the progression of thyroid disease.
Tips for Effective Thyroid Monitoring
- Maintain Regular Check-Ups: Schedule and keep regular appointments with your healthcare provider, even if you feel well.
- Keep a Health Diary: Document your symptoms, any changes in your body, and how you feel, which can be helpful during appointments.
- Stay Informed: Understanding the tests you are undergoing, and their purpose, can help you be more proactive about your health.
MEDICATION MANAGEMENT FOR THYROID HEALTH
Effective management of thyroid conditions often necessitates the use of specific medications. Understanding what medications are commonly used for various thyroid disorders, along with the importance of medication adherence, is crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes. Here we explore the key aspects of medication management for thyroid health, offering insights into how these therapies work and why they are essential.
Common Medications for Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism: The standard treatment for hypothyroidism involves synthetic thyroid hormone replacement, typically with levothyroxine (T4). This medication helps to restore normal hormone levels, alleviating symptoms of hypothyroidism such as fatigue, weight gain, and mood swings. Dosage is critically determined based on individual needs and TSH levels, which can vary significantly from one person to another.
Hyperthyroidism: Managing an overactive thyroid may require antithyroid medications such as Methimazole or Propylthiouracil, which help slow down the thyroid's hormone production. In some cases, beta-blockers like propranolol are prescribed temporarily to manage symptoms such as rapid heart rate and tremors associated with hyperthyroidism. For long-term management, radioactive iodine therapy or surgery might be considered, depending on the severity and the patient’s overall health.
The Importance of Medication Adherence
Medication adherence is fundamental in managing thyroid disorders effectively. Consistent use of prescribed medications as directed by a healthcare provider ensures that blood levels of thyroid hormones remain stable, which is essential for:
- Preventing Fluctuations: Inconsistent medication intake can lead to fluctuations in hormone levels, resulting in a return or worsening of symptoms.
- Optimizing Health Outcomes: Regular adherence to medication schedules maximizes the therapeutic benefits, enhancing overall health and quality of life.
- Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment: Regular follow-ups and thyroid function tests are needed to adjust the medication dosage accurately, a process that relies on consistent medication usage to be effective.
Tips for Enhancing Medication Adherence
- Routine Establishment: Taking your medication at the same time each day can help integrate it into your daily routine, reducing the likelihood of missing doses.
- Use Technology: Utilize Rouria’s app for medication reminders or set alarms on your phone to remind you when it is time to take your dose.
- Educate Yourself: Understanding the purpose and benefits of your medications, as well as potential side effects, can motivate adherence.
- Communicate with Your Healthcare Provider: Regular communication with your healthcare provider allows for adjustments in treatment if side effects occur or if your condition changes, which can also aid in adherence.
LIFESTYLE MODIFICATIONS FOR THYROID HEALTH
Managing thyroid health effectively often requires making thoughtful adjustments to your lifestyle. These modifications can significantly impact the function of your thyroid and your overall well-being. Here we delve deeper into the three critical areas of lifestyle changes—diet, exercise, and stress management—offering practical tips and reasons why these aspects are particularly important for those dealing with thyroid conditions.
Diet: Nourishing Your Thyroid

A balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing thyroid health. Here's how you can support your thyroid function with the right nutrients:
- Iodine: Essential for thyroid hormone production, iodine-rich foods like iodized salt, seafood, and dairy should be consumed in appropriate amounts. (Iodine is included for completeness; a lot of foods in the U.S. are iodine fortified.) Overconsumption or underconsumption of iodine can lead to thyroid imbalances.
- Selenium: This vital mineral activates thyroid hormones, making them available for your body's use. Incorporate selenium-rich foods such as Brazil nuts, tuna, and eggs into your diet to aid in efficient thyroid function.
- Zinc: Necessary for the synthesis of thyroid hormones, zinc can be found in beef, chicken, nuts, and legumes. Ensuring adequate zinc intake supports thyroid health.
- Vitamins A, D, and E: These vitamins are important for maintaining thyroid health. Vitamin A, found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach, supports thyroid hormone production. Vitamin D, available through sunlight exposure and foods like salmon and fortified dairy, regulates the immune system and thyroid function. Vitamin E, present in almonds, sunflower seeds, and spinach, protects the thyroid gland from oxidative damage.

Moderating the intake of goitrogenic foods such as broccoli, cauliflower, and kale, particularly when raw, is also recommended, as these can interfere with thyroid hormone production. Cooking these foods reduces their goitrogenic effect, making them safer for those with thyroid issues.
Exercise: Enhancing Thyroid Function Through Activity

Regular exercise is beneficial for thyroid health, helping to manage symptoms and enhance overall well-being:

- Boosts Metabolism: Physical activity stimulates metabolism, which is often regulated by thyroid hormones, aiding in effective weight management.
- Improves Energy Levels: Combat the fatigue commonly associated with thyroid disorders through regular exercise, which helps elevate energy levels.
- Mood Enhancement: Engaging in exercise releases endorphins, natural mood lifters that can alleviate depression or mood swings linked to thyroid conditions.
It is important to start with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase the intensity as your body adapts, especially if you experience joint pain or fatigue.
A word of caution: Those with untreated hyperthyroidism should avoid strenuous activity as this puts to much strain on their hearts.
Stress Management: Protecting Your Thyroid from Stress Overload
Managing stress is key to maintaining thyroid function and preventing exacerbations of thyroid disease:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: These practices are powerful tools for centering thoughts and calming the mind, reducing stress's impact on thyroid health.
- Yoga: This holistic approach combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to significantly reduce stress levels and improve overall health.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing good sleep hygiene is essential, as lack of sleep can worsen stress and thyroid symptoms.
Implementing these stress management strategies not only helps in maintaining thyroid health but also enhances your body’s overall resilience to stress-related complications.
Sleep: Supporting Thyroid Health Through Restful Nights
Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining thyroid function and overall well-being:
- Aim for 7-9 Hours: Prioritizing 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night is important for allowing your body to rest and repair, aiding in optimal thyroid function.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body's internal clock, promoting sleep quality and thyroid health.
- Sleep Environment: Creating a restful sleep environment by keeping your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet can enhance sleep quality, supporting your thyroid function.
- Relaxation Techniques: Relaxation activities before bed, such as reading or listening to calming music, can help prepare your body for sleep and improve overall health.
Hydration: Keeping Your Thyroid Functioning Optimally
Staying properly hydrated is important for supporting thyroid health and metabolic processes:
- Daily Water Intake: Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water daily to maintain adequate hydration levels, which are vital for thyroid hormone production and function.
- Hydrating Foods: Incorporate hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables into your diet to support overall hydration and thyroid health.
- Limit Dehydrating Substances: Reduce the intake of caffeine and alcohol, as they can lead to dehydration and negatively impact thyroid function.
CONCLUSION
Effectively managing thyroid health requires an integrated approach that combines lifestyle changes, medication, regular monitoring, and both telehealth and in-person medical consultations. By understanding and implementing these strategies, individuals with thyroid disorders can lead healthy, active lives. Educating yourself about your thyroid condition and active participation in your treatment plan is fundamental. Resources such as patient support groups, reliable online information, and ongoing communication with your healthcare provider can enhance understanding and management of your thyroid health.
What are the key symptoms of thyroid dysfunction?
Thyroid dysfunction symptoms vary but typically include changes in weight, mood swings, altered energy levels, and sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to quicker diagnosis and management.
How can diet affect thyroid health?
What are the best exercises for managing thyroid health?
How does stress influence thyroid function?
What medications are commonly used for treating hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Why is regular monitoring important in thyroid health management?
. Can thyroid disorders be completely cured?
What are the signs that indicate you should see a thyroid specialist?
How do thyroid problems affect pregnancy?
What lifestyle changes can help manage thyroid health?